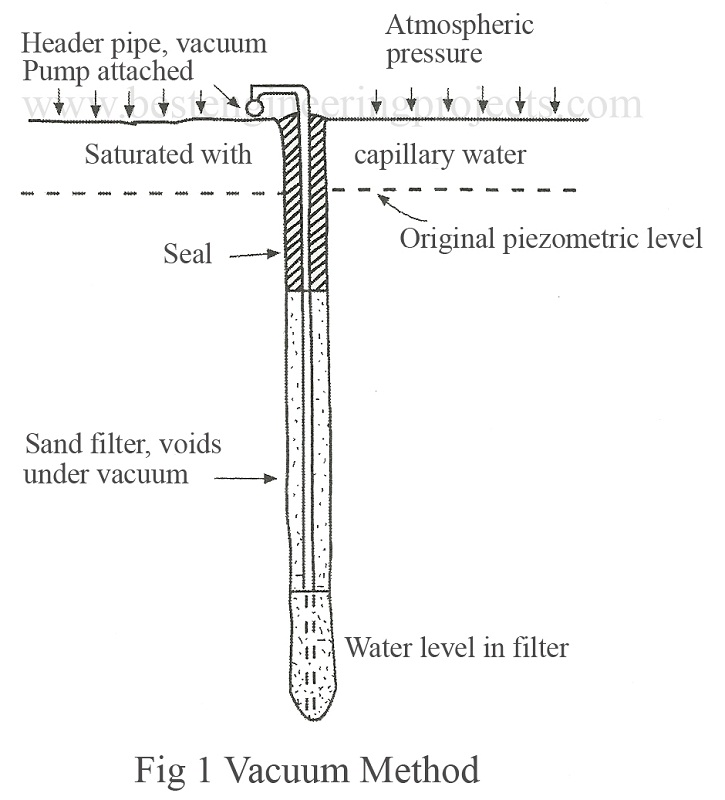
If the effective size of the soil to be drained is less than 0.05 mm, well points cannot be used because capillary forces prevent flow. In order to drain such soils suction head in excess of capillary head is to be applied i.e. by vacuum method. The typical soils of such nature are sands and silty sands. These soils possesses, coefficient of permeability between 1 ×10-3 to 1 ×10-5 cm/sec. Drainage in such cases can be made efficient by the use of vacuum well points as in Fig.1.
Vacuum well points are installed by jetting well points into the ground. The well points are spaced every one-meter. Sand is poured in the hole in such a way that the top l m of the hole remains unfilled. The top l m of the hole is filled by clay and tamped. Well points are placed at a closer spacing than in a conventional system. Vacuum method is applied in the sand filter around the hole by connecting the header pipe to a vacuum pump, which run continuously and a pressure deficiency is created between water table and the soil to be drained. The atmospheric pressure squeezes water out of voids due to consolidation and gets collected in the borehole. The collected water is pumped intermittently. Due to consolidation, the effective pressure is increased and consequently the shear resistance of the soil is increased.